Swallow Week 2024: Citizen Science
Citizen Science and Swallows: How Every Observation Counts

Tree Swallows in Alaska
Swallows, those aerial acrobats that delight us with their graceful flight, play a significant role in ecosystems around the world. Beyond their interesting antics and dapper good looks, swallows are a fascinating subject for study for citizen scientists. Citizen science projects involving swallows offer bird enthusiasts of all ages the chance to contribute to the conservation and understanding of these birds. Whether you’re a seasoned birdwatcher or just starting to explore the avian world, there are a few opportunities to get involved.
Alaska Swallow Monitoring Network
Scientists and citizens team up to monitor Tree Swallows in Alaska, to study their phenology (the timing of seasonal behaviors and cues) and how climate change impacts nesting and other activities. Monitoring occurs at several locations across Alaska with nest boxes installed in appropriate habitat. More Info →
Swallows and Swifts in Italy
Rondini & Co uses iNaturalist to compile observations of swallow and swift species in Trento, Italy. The data is mainly input by students in the region. More Info →
NestWatch
NestWatch is a citizen science effort from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Participants monitor nests throughout the breeding season, following safety and interval protocols. Nests of virtually any species can be monitored, including commonly submitted species Tree Swallow, Violet-green Swallow, and Barn Swallow. More Info →
Purple Martins are unique in that they are almost entirely dependent on human-provided housing for nesting in the eastern parts of North America. They nest in colonies and prefer multi-compartment birdhouses or gourds strung up on poles in open areas, a nesting habit that has developed over generations of interaction with humans. Due to this reliance on humans for nesting sites, there are several citizen science projects that involve the study of Purple Martins.
Project Martinwatch
Project Martinwatch is an effort to both improve management of Purple Martin (PUMA) colonies, and to track the reproductive biology of PUMAs. Data is collected by PUMA landlords or citizen scientists who help landlords with monitoring. Participation is easy and involves performing nest checks every 5-7 days from nest building to fledgling and submitting your data at the end of the season. More Info →
Purple Martin Scout-Arrival Study
This study aims to gather data on first arrival times of Purple Martins to nesting sites. This data, usually submitted by PUMA landlords, tracks the progress of springtime migration of Purple Martins across North America. The historical and real-time information is helpful to landlords to know when to open up their colonies to nesting birds. More Info →
Purple Martin Banding
While untrained citizen scientists cannot legally band birds without a federal permit, landlords can contact their local Audubon Society, state wildlife agency, or birding club to locate an appropriate banding program, if one exists. If you find a banded Purple Martin (or any other banded bird), you can report it to the Bird Banding Laboratory. More Info →
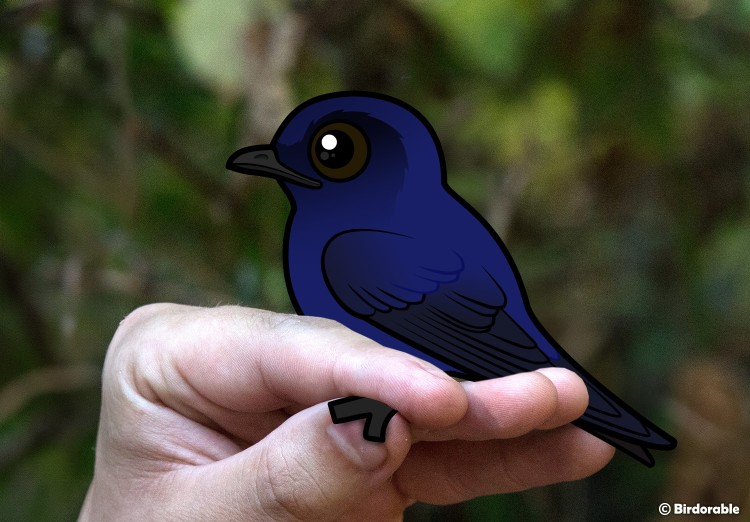

Purple Martin getting banded
Participating in these projects not only provides valuable data to scientists but also enriches the participant's understanding and appreciation of swallows and martins. The firsthand experience of monitoring these birds fosters a deeper connection with nature and promotes conservation efforts on a personal level.
For those looking to get involved, reaching out to local birding clubs, wildlife organizations, or online platforms dedicated to citizen science is a great start. Besides these projects, entering sighting data of the swallows and other birds you find into eBird is a great way to contribute to citizen science on a regular basis.